
|

Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) - Supplier Business Diagnostics
Supplier Relationship Mangement (SRM) Business Diagnostics
Supplier Business Diagnostics are a key element of a proactive Supplier Relationship Management used as a prelude to delivering step-changes in performance. Essentially this is about getting inside the supplier's business and working with them to find improvement opportunities. It takes a considerable amount of trust between customer and supplier and is best served by establishing a clear savings sharing policy before-hand.
Risks to the Supplier
One of the supplier's key concerns will be that by coming inside their business their customer will develop a better understanding of their cost model and this will threaten their margin. Presumably for this reason, Nissan's lean supplier development teams have historically come into their suppliers and instead of working on manufacturing lines supplying their own products, they have elected to work in conjunction with a continuous improvement team, set up for that purpose, on manufacturing lines for their competitors! This builds good-will and enables Nissan to transfer a certain amount of their lean expertise into their suppliers in a non-threatening collaborative manner.
Another way of addressing this issue is to focus all efforts on reducing costs, not margins, and communicate this intention from the outset.
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) Business Diagnostic Case Example
- Customer (and Client): First tier automotive supplier of wiring harnesses
- Supplier: Polymer Coumpounder
Background
- Supplier was in a loss making situation, running at full capacity
Obective of the SRM Business Diagnostic Project
- Identify substantial savings opportunities.
- Develop open book cost model
Scope
- Entire business diagnostic (manufacturing and supporting operations) and customer's internal acquisition costs.
Team
- Supplier's Sales Director (P/T)
- Customer's Buyer (F/T)
- Customer's Finance Manager (P/T) to develop the cost model
- Lean Process Re-engineering Supplier Development Consultant* (F/T)
* my role.
Results
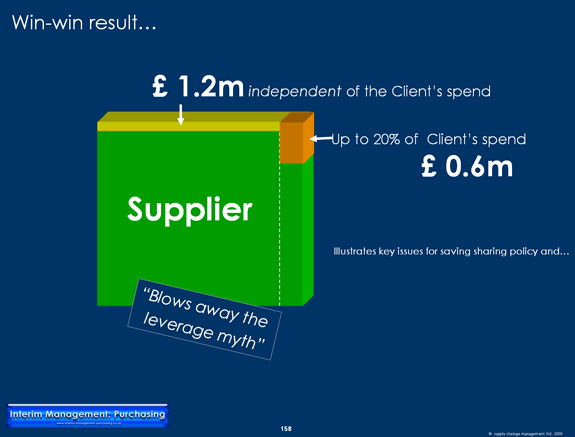
- Savings opportunities of up to £ 1.8m identified and agreed by supplier
- Open book cost model developed
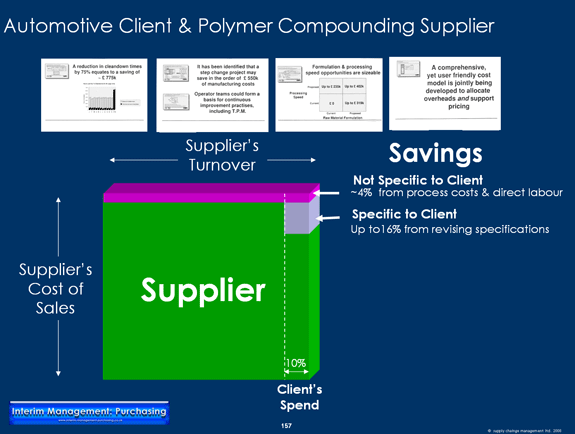
Supplier Development Savings Identified
- ~ £ 750k from the introduction of SMED techniques to reduce changeover times - the supplier was running at full capacity. SMED would provide additional capacity which could be filled readily.
- 30% reduction in direct labour - justified by a activity / transaction analysis
- Up to 16% savings in value engineering the raw material specification
The above savings were accepted by the suppliers' executive management team.
Skills Required for Supplier Business Diagnostics
Self evidently, the required skill-set for a diagnostic depends on how broad its scope will be. Many manufacturing customers focus their supplier development activities just on applying lean process re-engineering principles to the manufacturing operations of their suppliers. However, the same principles can be applied to supporting business processes. All too typically these have evolved incrementally and have accumulated considerable waste; which can also be addressed.
Savings Sharing Policies
It's best before embarking on a Supplier Business Diagnostic to have agreement beforehand about the savings sharing policy. As this example shows, savings opportunities can affect other customers of the supplier too. For this reason it's a misnoma that if you don't have a big enough proportion of your supplier's business that the supplier's incentive for your combined engagement won't be worth it. In the case example below, savings opportunities for the supplier were substantially greater than for my first tier automotive client. So, rather than agreeing to share the savings say 50/50 or 60/40, it may be appropriate to propose a savings sharing policy that says the supplier takes X% of any savings associated with other customers and the customer (facilitating the identification and delivery of the savings) takes 100%-X%. Furthermore, for savings which are specific to the customer, the customer takes X% and the supplier 100%-X%. Its worthwhile enshrining these or alternative savings sharing principles in supply contracts, when these are awared, establishing the precedent long before the issue potentially comes up for debate.
Case Examples of SRM Improvements During Interim Management Assignments
For more case examples of tools for step change supplier performance transformations, the following pages are worth reviewing:
Once any substantial step-change performance gaps have been closed, supplier scorecards can be used to drive continuous improvement.
More Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) Information
© www .interim-management-purchasing.co.uk December 2012
|


The polymer compounding supplier involved in this particular Supplier Business Diagnostic was a joint venture between ICI and Enichem.
Following the conclusion of this successful assignment the client, a first tier automotive wiring systems manufacturer, requested additional consultancy support to deploy the same approach on another major supplier of rubber mouldings. |

